Hello EveryOne, Hope you all are doing well. So today's Our topic is Docker. If you know about Docker then it is a good thing and in this, we will learn something new if you don't know about it then don't get panic after reading the blog, of course, you will get.....
Basic of Docker
How to install Docker
Why we need Docker
How it use in real-life
Let's Start Today's Session....
What is Docker?
\=>Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications.
\=>Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly.
\=>With the help of Docker, you can manage your infrastructure in the same ways you manage your applications.
\=> By taking advantage of Docker’s methodologies for shipping, testing, and deploying code quickly, you can significantly reduce the delay between writing code and running it in production.
Basics of Docker:-
Docker was first released in March 2013. It is developed by Solomon Hykes and Sebastien Paul.
Docker uses the container on the host Operating System to run the application. It allows applications to use the same Linux Kernel as a system on the host computer, rather than creating a whole virtual Operating System.
We can install Docker on any Operating System but the Docker engine runs natively on Linux distribution.
Docker us written in the 'GO' language.
Docker is a tool that performs Operating System level virtualization, also known as containerization.
why we need Docker .. Before Docker, many users face the problem that a particular code runs in the developer's system but not in the user's system.
Advantages of Docker:
No pre-allocation of RAM
CI Efficiency => Docker enables you to build a container image and use that same image across every step of the deployment process
Less Cost
It is light in weight
It can run on physical hardware, virtual hardware, or on cloud
You can re-use the image.
It took very less time to create the container.
Note: When an image is running we can say container, when we send a container or not-runnable state we can say Image.
Disadvantages of Docker
Docker is not a good solution for application that requires a rich GUI.
It is challenging to handle several containers.
Because Docker does not offer cross-platform compatibility, an application created to run in a Windows Docker container cannot operate on Linux, and the opposite is also true.
When the development and testing operating systems are the same, Docker is appropriate; if not, virtual machines should be used.
No data recovery or backup solution.
Architecture of Docker:-

Components of Docker:
Docker Daemon:-
Docker Daemon runs on the Host Operating System.
It is responsible for running containers and managing docker services.
Docker Daemon can communicate with other daemons
Docker Client:
Docker users can interact with the docker daemon through a client.
Docker client uses commands and Rest API to communicate with the docker daemon.
When a client runs any server commands on the docker client terminal, the client terminal sends the docker commands to the docker daemon.
Docker clients can communicate with more than one Daemon.
Docker Host:
Application execution and running environments are provided by Docker hosts. The Docker Daemon, Images, Containers, Network, and Storage are all present.
Docker Hub/ Registry:
Docker Hub manages and stores the Docker Images.
There are two types of hub in the Docker..
Public Hub:- Public hub also called Docker Hub.
Private Hub :- It is used to share images within the enterprise.
Docker Images:
Docker images are the read-only binary templates used to create docker containers.or a single file with all dependencies and configurations required to run a program.
Ways to create an image:
Take an image from the Docker Hub.
Create an image from Dockerfile
Create an image from existing docker containers.
Docker Container:
The container holds the entire package that is needed to run the applications.
In other words, We can say that the image is a template and the container is a copy of the template.
Containers is like virtualization when they run on the Docker engine.
Images Become containers when they run on the docker engine.
When we build the Dockerfile then the Docker Image was made and when we run the Docker Image Container came.
Docker Installation and important commands:
❖How to install Docker in Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker.io
❖To see all the images present in your local:
docker images
❖To find out images in the Docker Hub:
docker search <image name>
❖To download an image from Docker-hub to a local machine:
docker pull <image Name>
❖To give a name to the container and run:
docker run -it --name <container name> <image name>
-it: it used for Interactive Mode and Direct to terminal
❖To check, whether the service is Strating or Not:
service docker status
service docker info
❖To start the service:
service docker start
❖To start/stop the container:
docker start <container name>
docker stop <container name>
❖To go inside the containers:
docker attach <container name>
❖To see all the containers:
docker ps -a
❖To see only running containers:
docker ps
❖To stop the container:
docker stop <container name>
❖To delete the container:
docker rm <container name>
docker kill <container name/ID>
❖Exiting from the docker container:
exit
❖To delete the images:
docker images rm <image name>
If you confuse in the commands then don't get panic I will discuss every command with the help of project in this blog only...
How to create a Dockerfile:
First we will know about what is Dockerfile
☛Dockerfile is a text file it contains some set of instructions.
☛Automation of docker image creation.
❏FROM
For the base image. This command must be on top of the dockerfile.
❏RUN
To execute commands, it will create a layer in the image.
❏MAINTAINER
Author/Owner/Description
❏COPY
Copy files from the local system (Docker VM) we need to provide a source, and destination.
❏ADD
Similar to copy, It provides a feature to download files from the internet, also we extract the file from the docker image inside.
❏EXPOSE
TO expose ports such as 8080 for Tomcat, port 80 for Nginx etc..
❏WORKDIR:
To set working directory for a container.
❏CMD
Execute commands but during container creation.
❏ENTRYPOINT
Similar to CMD, but has higher priority over CMD, the first commands will be executed by ENTRYPOINT only.
❏ENV
Environment variables.
❏ARG
To define the name of a parameter and its default value, the difference between ENV and ARG is that after you set on env using ARG you will not be able to access that late on when you try to run the Docker container.
Creation of Dockerfile--
Create a file named Dockerfile
Add instructions in Dockerfile
Build a Docker file to create an image
Run Image to create the container
Let's understand by simple react application, if you want this application you can fork from my GitHub account.
By clicking on this you will transfer to my github account.
Let's Start first we create a Dockerfile using Vi editor for Linux.
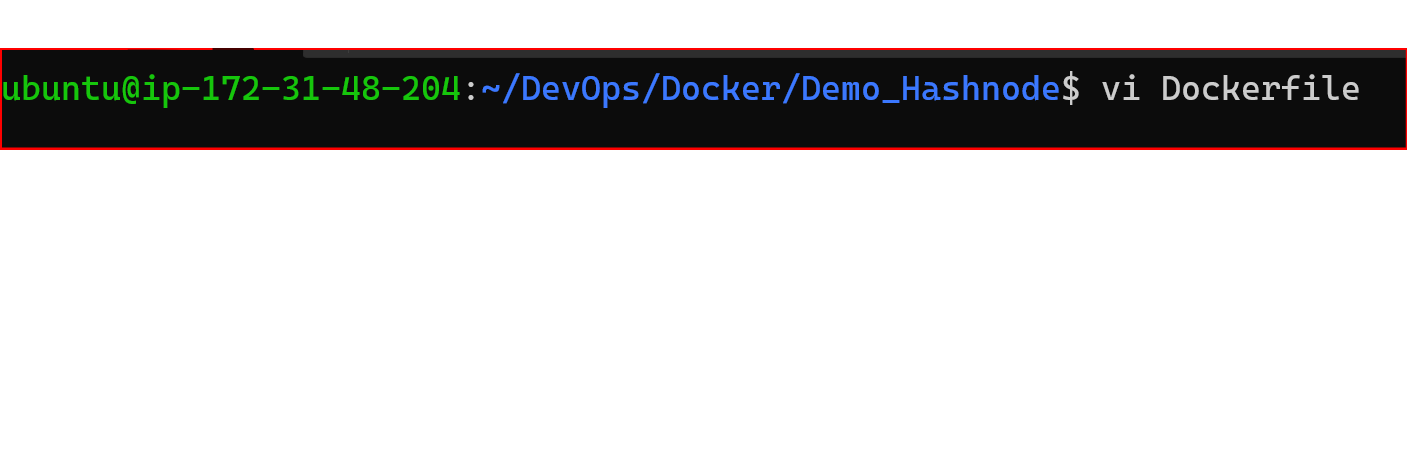
Now we will write some commands in our Docker file.
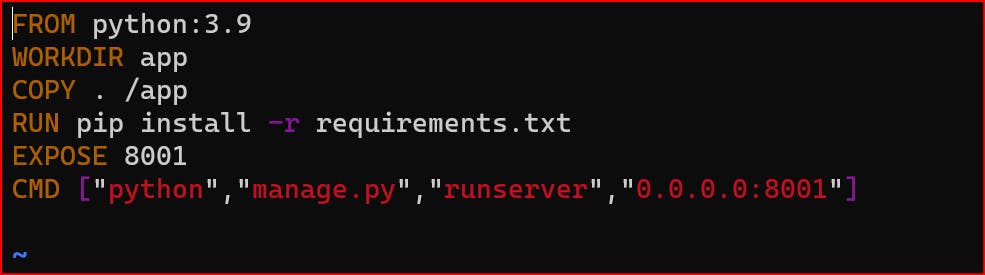
here we use FROM because the application based on the python so we want bash image of Python
After this we use WORKDIR for where all the containers file will be stored, Copy command is use to copy the current data to the app directory
RUN command is used to installing all the required packages.
Expose command is used because we are exposing our port to 8001
CMD is used for run the Python and manage.py file.

Now we build image from the Dockerfile using command
docker build -t react-django-app:latest
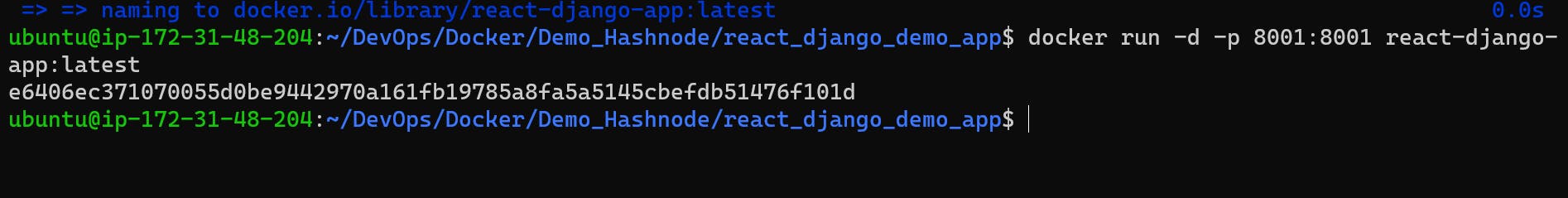
Now we run our image and make container..
docker run -d -p 8001:8001 react-django-app:latest
Tp run on the port we want to give permission to 8001 using security group of was
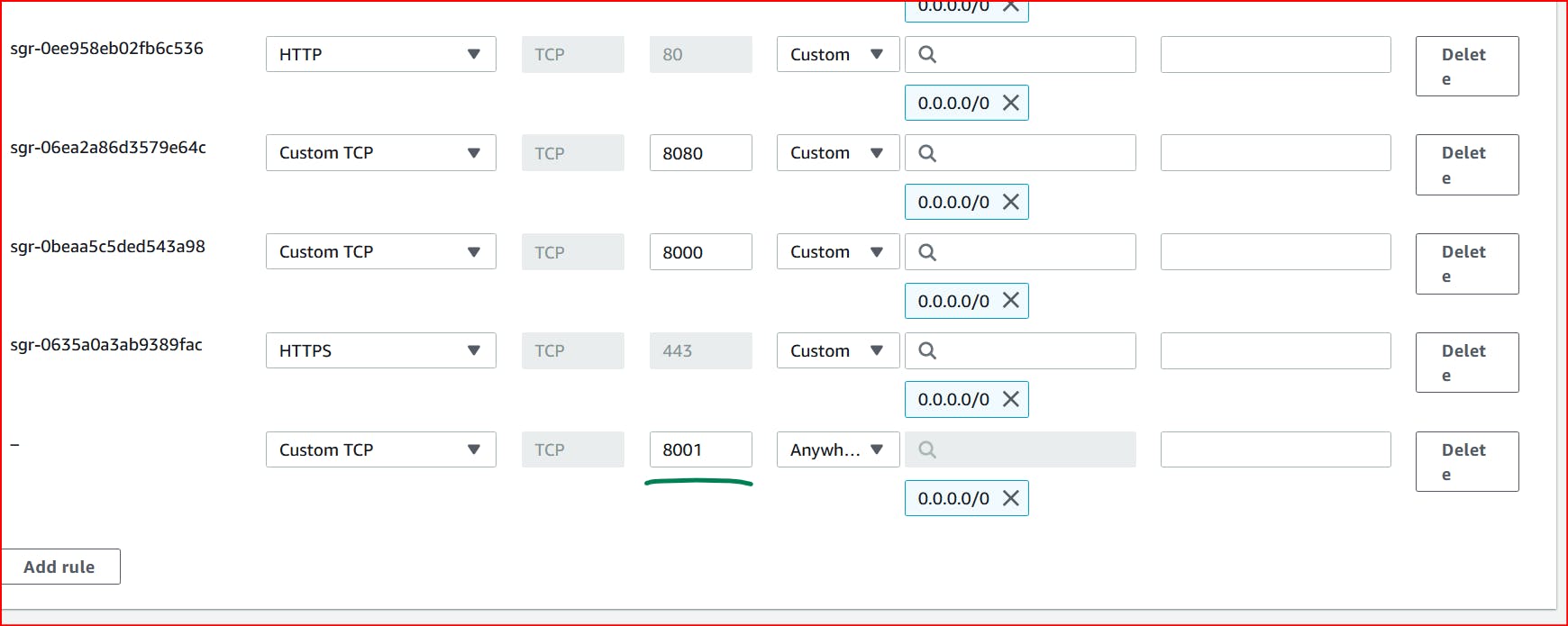
Now our app will run on the server let's check ..
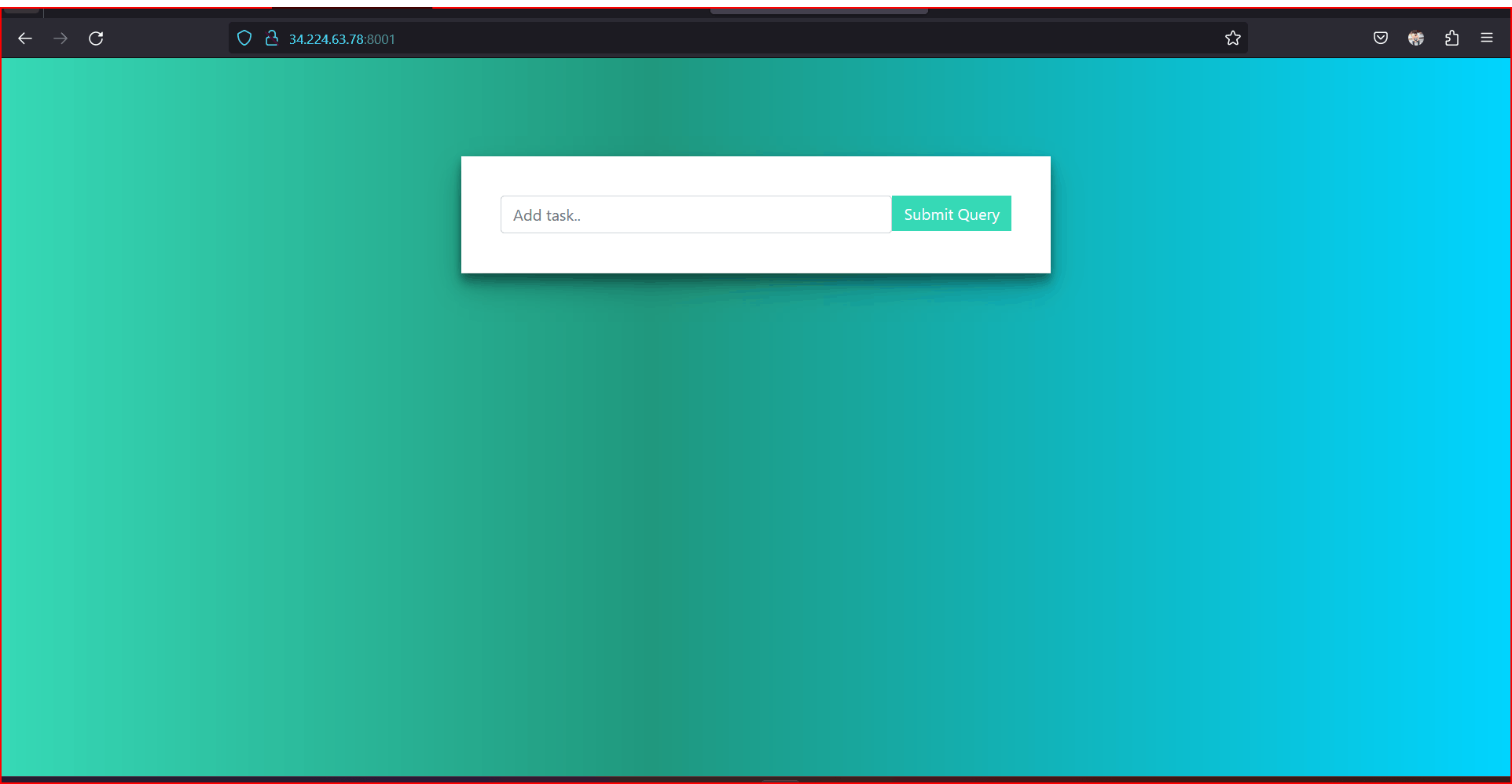
Our app is running properly ...
Thanks for reading this blog if you like this blog the please like and comment and for advance docker like docker volume , docker swarm then my next blog will be on that..
Keep Learning ..
:) Happy Learning...
